Using dlt (data load tool) in Microsoft Fabric

The open-source Python library dlt streamlines data engineering by automatically normalizing messy, dynamic data into structured tables with built-in schema inference and evolution. It empowers developers to build robust, self-healing extraction and loading pipelines rapidly, eliminating the maintenance burden of handling changing data structures and API endpoints.
A co-worker recently asked me if we had ever used dlt inside a Python notebook in Microsoft Fabric to land data into Delta tables within a Lakehouse. I hadn’t seen it implemented myself and quickly took to Google to see if I could find any articles walking through how to do it.
I couldn’t find one.
“Ok, that’s weird..” I thought to myself. I look through dlt’s documentation, and they seem to support all the things that I’d expect — Delta Lake as a destination and Azure storage connectivity. So, I figured that I would just install dlt with pip install try and build an example from the docs.
I setup my pipeline to load some sample data into a Delta table inside a Lakehouse and quickly ran into a few problems.
Problem #1
I start getting the error: Last failure message was: type object 'DeltaTable' has no attribute 'is_deltatable' . This is due to an older version of the Python deltalake package that comes pre-installed with Fabric Python notebooks.
The resolution here was to add deltalake to the pip install and add --upgrade at the end
Problem #2
Receiving new errors: Last failure message was: Generic LocalFileSystem error ↳ Unable to rename file ↳ Function not implemented (os error 38). This appears to be a limitation around using the mounted storage path /lakehouse/default/Tables/dbo
I switched to using the abfss:// path to the schema and was met with new errors: <class 'NotImplementedError'> Cannot request details when using fsspec.glob. For adlfs (Azure) please use version 2023.9.0 or later
To get this working, I had to update my pip install to include the az dependencies for dlt:
pip install "dlt[az]" deltalake -q --upgrade
Problem #3
Although the table was written to the Tables section of the Lakehouse, because dlt includes some other file data within the dataset, this caused the Fabric Lakehouse to not correctly identify the table:
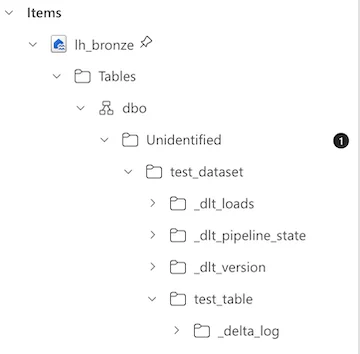
Here is the workaround I came up with to get the table to show up in Tables but still allow dlt to keep all of the other files about state/loads/versioning.
- Land the data into the Files section of the Lakehouse
- Use
semantic-link-labsto automate the creation of the OneLake table Shortcut to the appropriate location.
Full Solution
Below you will find all the python code to get you going in terms of using dlt to load to Delta tables in Microsoft Fabric Lakehouses, using a very basic sample dataset. I hope you find this to be helpful!
# In[1]:
pip install "dlt[az]" deltalake semantic-link-labs -q --upgrade
# In[2]:
import dlt
import json
import notebookutils
token = notebookutils.credentials.getToken("storage")
TABLE_NAME = "test_table"
@dlt.resource(table_name=TABLE_NAME)
def sample_data():
yield from [
{"id": 1, "name": "Alice", "value": 100},
{"id": 2, "name": "Bob", "value": 200},
]
################################################################################################
# dlt loads metadata files around the delta table folder. Landing directly in the "Tables"
# section of the Lakehouse will result in the folder created being an "Unidentified" table.
# We want to write to the Files section of the Lakehouse to preserve the dlt metadata files.
# Later, we will create a shortcut to that delta table so that it appears cleanly in "Tables"
################################################################################################
LAKEHOUSE_PATH = "abfss://<YOUR_WORKSPACE_GUID_HERE>@onelake.dfs.fabric.microsoft.com/<YOUR_LAKEHOUSE_GUID_HERE>/Files/dlt_test"
fs_dest = dlt.destinations.filesystem(
bucket_url=LAKEHOUSE_PATH,
credentials={
"azure_storage_account_name": "onelake",
"azure_storage_sas_token": token, # fsspec/adlfs accepts token here
},
# These get passed to deltalake's write_deltalake for delta table writes
deltalake_storage_options={
"bearer_token": token,
"use_fabric_endpoint": "true",
}
)
DATASET_NAME = "test_dataset"
pipeline = dlt.pipeline(
pipeline_name="bronze_loader",
destination=fs_dest,
dataset_name=DATASET_NAME
)
load_info = pipeline.run(sample_data(), table_format="delta")
print("\n")
print(load_info)
# In[3]:
from sempy_labs import lakehouse
lakehouse.create_shortcut_onelake(
table_name=TABLE_NAME,
source_lakehouse="<YOUR_LAKEHOUSE_NAME_HERE>",
source_workspace="<YOUR_WORKSPACE_NAME_HERE>",
source_path=f"Files/dlt_test/{DATASET_NAME}",
destination_path=f"Tables/dbo"
)
# In[4]:
import polars as pl
## This path assumes that the lakehouse where the shortcut was created is the Notebook's default LH
table_path = f"/lakehouse/default/Tables/dbo/{TABLE_NAME}"
df = pl.read_delta(table_path)
# Verify that we can query the data from the Table path
display(df)
